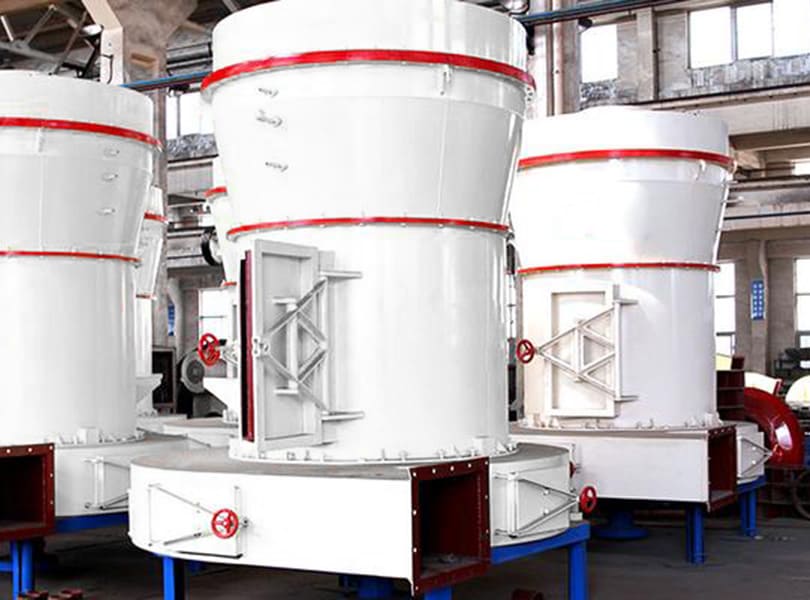
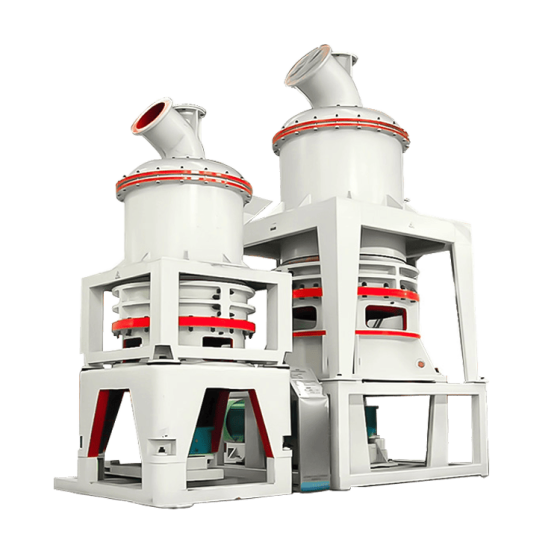
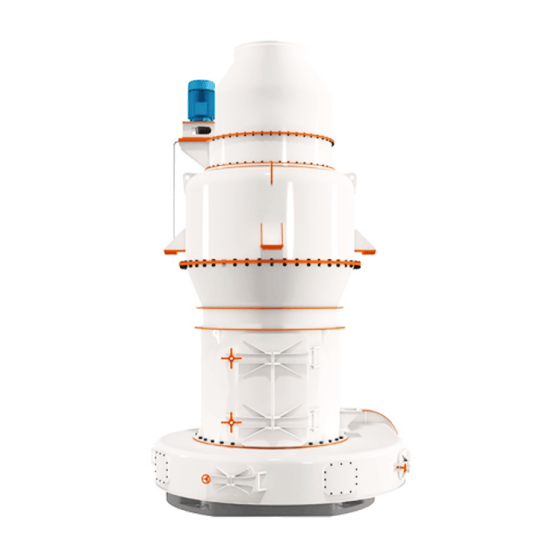
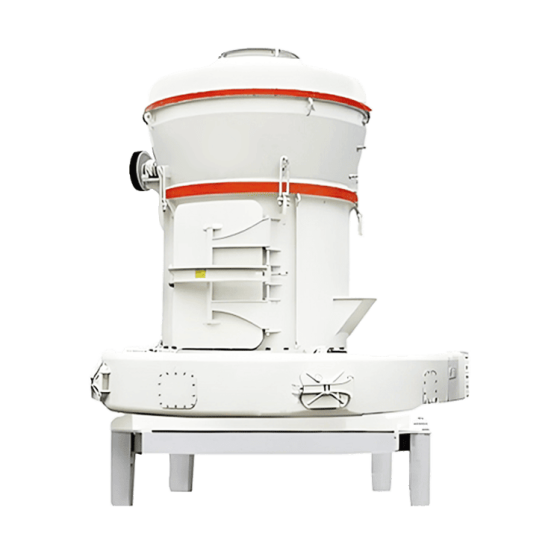
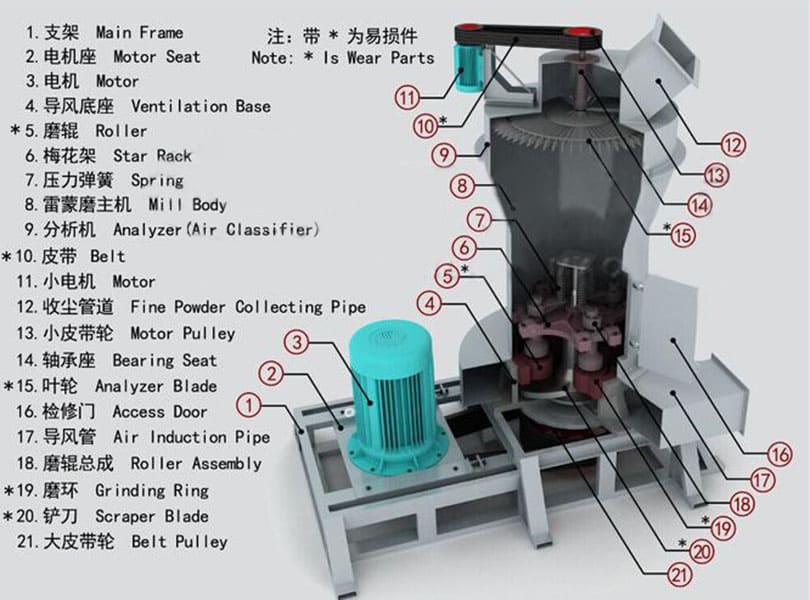
Raymond Mill is a powder processing equipment widely used in mining, building materials, chemical industry and other industries. It is mainly used for efficient grinding of non-flammable and explosive materials with Mohs hardness ≤ 9.3 and humidity below 6%. The finished product particle size range is usually between 80-325 mesh (0.045-0.18mm). Its core function is to crush bulk materials into fine powder to meet the requirements of powder fineness and uniformity in industrial production.
Technical Features
1. High efficiency and energy saving
• It adopts a three-dimensional structure design, occupies a small area, has a highly integrated systematic production process (crushing → grinding → grading → powder collection), and reduces energy consumption by 30%-40% compared with traditional ball mills.
2. High grading accuracy
• The analyzer adopts variable frequency speed regulation technology, which can accurately adjust the particle size of the finished product (flexibly adjusted within the range of 80-325 mesh), with concentrated particle distribution and uniform fineness.
3. Strong reliability
• Key components (grinding roller, grinding ring) are made of high manganese steel or wear-resistant alloy materials with long service life; the transmission system is sealed to avoid dust intrusion and reduce failure rate.
4. High degree of automation
• Equipped with PLC control system, it can realize automatic adjustment of feed amount, air volume and classification speed, with easy operation and good stability.
5. Environmentally friendly and low noise
• It operates in a fully enclosed negative pressure environment and is equipped with a high-efficiency dust removal device. The dust emission concentration is lower than the national environmental protection standard. The equipment has low vibration and noise.
6. Strong adaptability
• It can process hundreds of materials such as limestone, calcite, barite, bentonite, gypsum, etc., and is particularly efficient for materials with medium and low hardness.
Typical Application Areas
• Mining: Powdering of metal and non-metallic minerals (such as calcium carbonate and talcum powder).
• Building materials: preparation of cement raw materials, coal powder and ceramic raw materials.
• Chemical industry: ultrafine grinding of pesticides, fertilizers, coating fillers.
• Metallurgy: processing of slag powder and refractory materials.
 crusherfactory.com
crusherfactory.com